The Galaxy S III is
making some serious inroads with development that seems to be
speeding up with every step. The latest big news to hit SGS3 users is
Ubuntu and Backtrack Linux being booted onto the device. Honestly, I
don’t personally see the point of using Linux on an Android device,
but if it’s Android and you’re a true geek, having the option and
being actually able to pull it off, is a feat on its own. As for the
procedure, we have XDA -Developers forum member tiborri to thank for
jotting up a tutorial, and of course, a few pieces of the tutorials
have actually been borrowed from other tutorials. So if you have
patience and are familiar with executing scripts, read on after the
break to learn more about how you can get Linux running on your
Galaxy S III.
All images below are
courtesy of tiborr.
To start off, you
will be needing an app called, Ubuntu Installer Complete LinuxInstaller developed by zackthespack. This app once launched, will
allow you to download and install 3 more apps that are required to
get Ubuntu up and running on the device:
- VNC Viewer
- Android Terminal Emulator
- Busybox
Needless to say your
device needs to be rooted for this app to function properly. If you
haven’t already done so, view our rooting guide for the Galaxy S
III here. That done, to avoid any issues, install the Omega ROM
featured here. Make sure USB debugging is enabled on the device. Now
run the app and download the Ubuntu file.
You will now need to
run a script that was originally written by zacthespack (download).
Once this is downloaded, copy this script (ubuntu.sh) and the ubuntu
file downloaded via Ubuntu Installer onto the internal memory of the
phone in a folder named Ubuntu.
With all the data in
its place, you now need to run the Android Terminal, and enter the
following commands:
su cd /sdcard/ubuntu sh ubuntu.sh
Now you will be
asked to input the resolution of your device, so in the case of SGS
3, enter in 1280×720.
You will now be asked to set this resolution as default. Press Y.
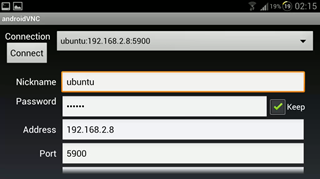
If you’re asked to put in a password, type in Ubuntu and press enter. Proceed to running the VNC Viewer and enter in the following settings as displayed in the screenshots below.




0 comments:
Post a Comment